Manganese In Well Water Removal
In the present research paper a biosorptive remediation practice for an aqueous medium sample polluted with manganese ions was implemented using the activated coastal waste of the zostera marina plant.

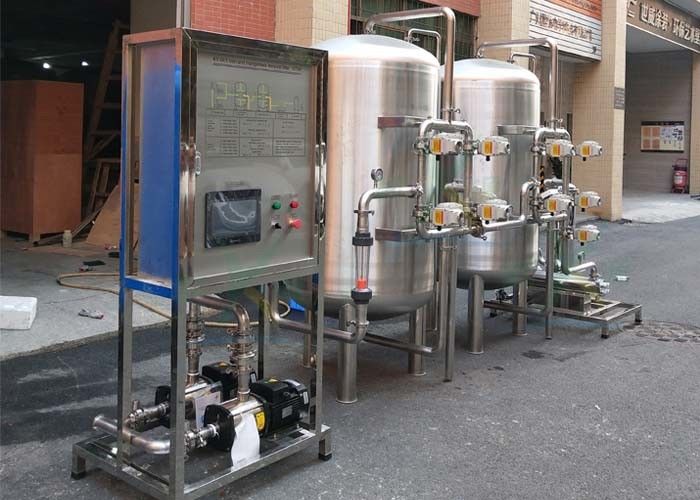
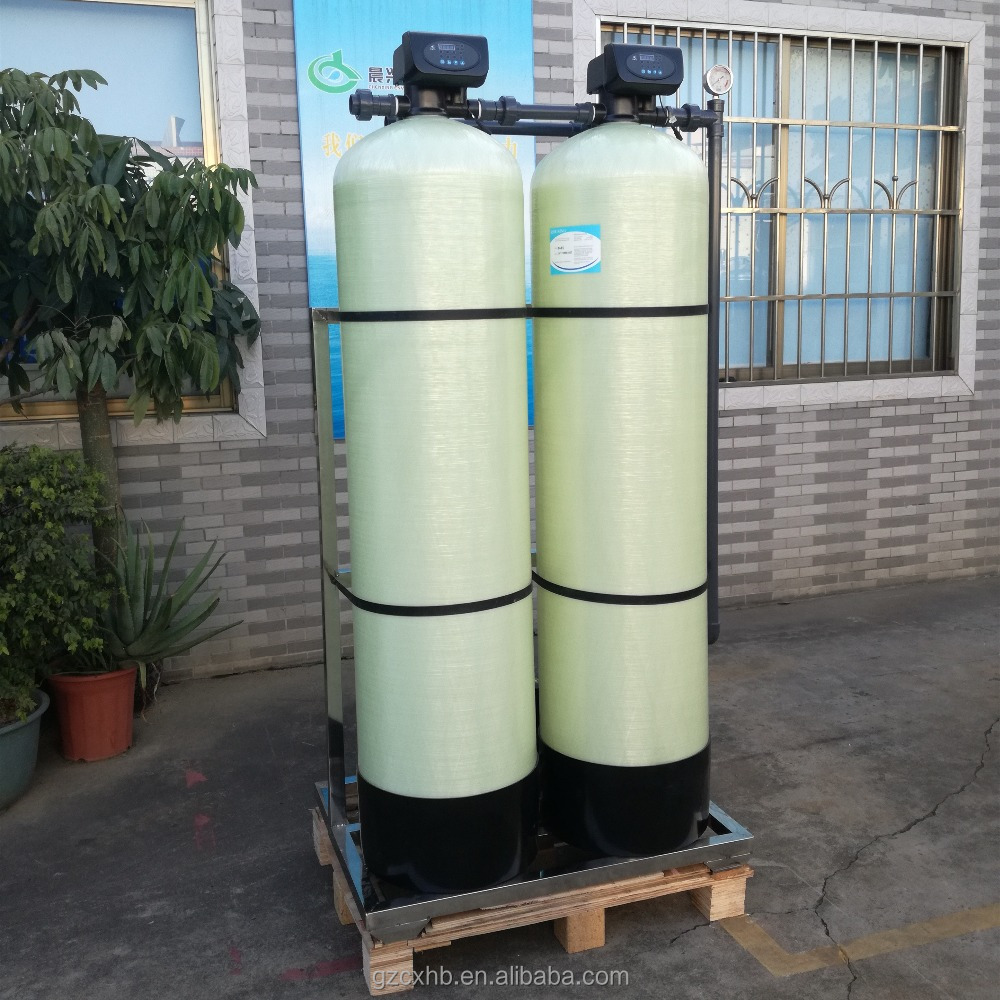
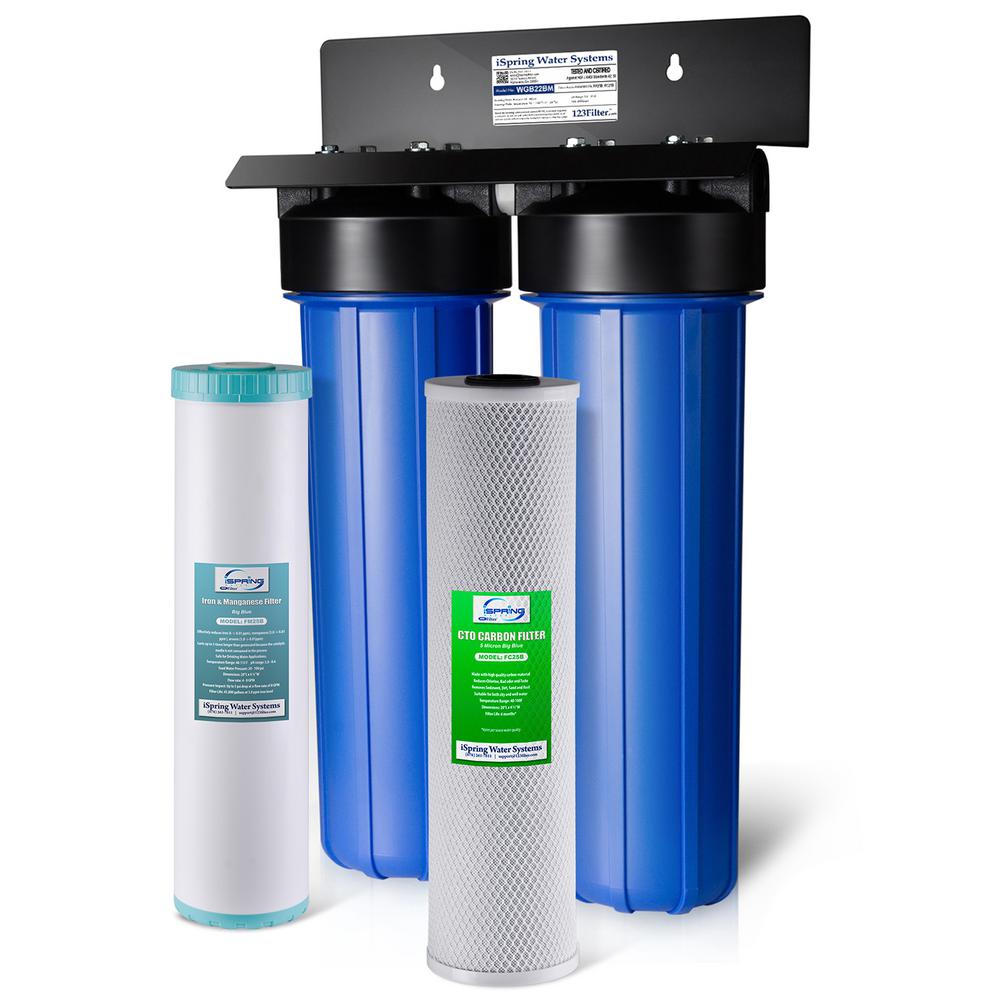
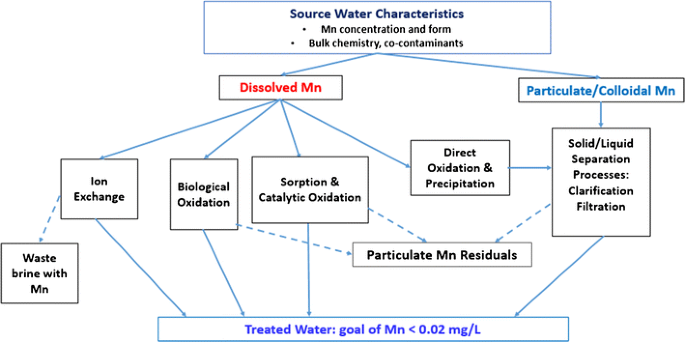
Manganese in well water removal. A water softener is typically used to treat hard water but it can also remove small amounts of reduced iron and manganese. Manganese and iron removal can be achieved similarly by exchanging manganese and iron with sodium. Water containing iron and manganese. Manganese removal in the water treatment process using.
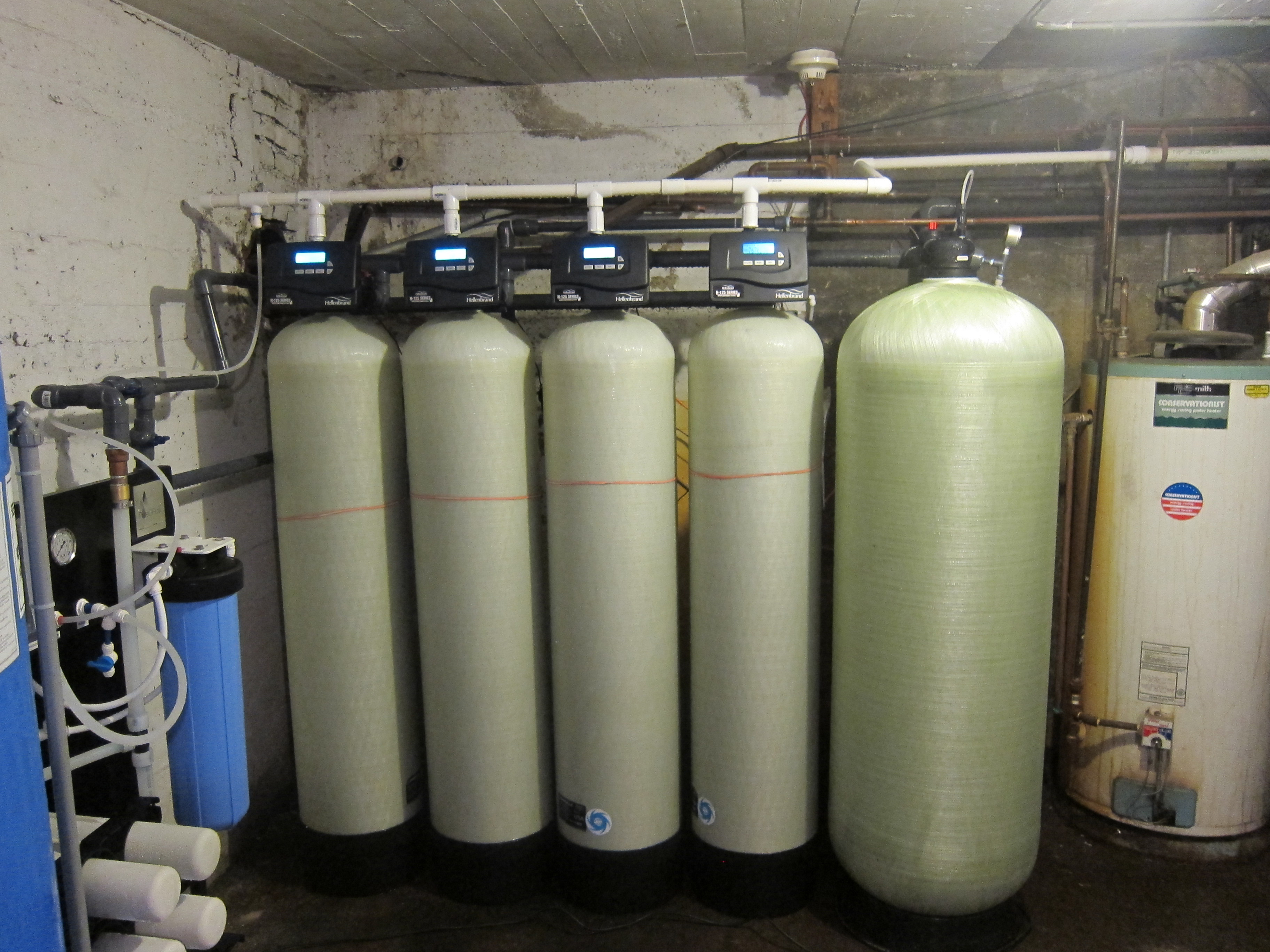
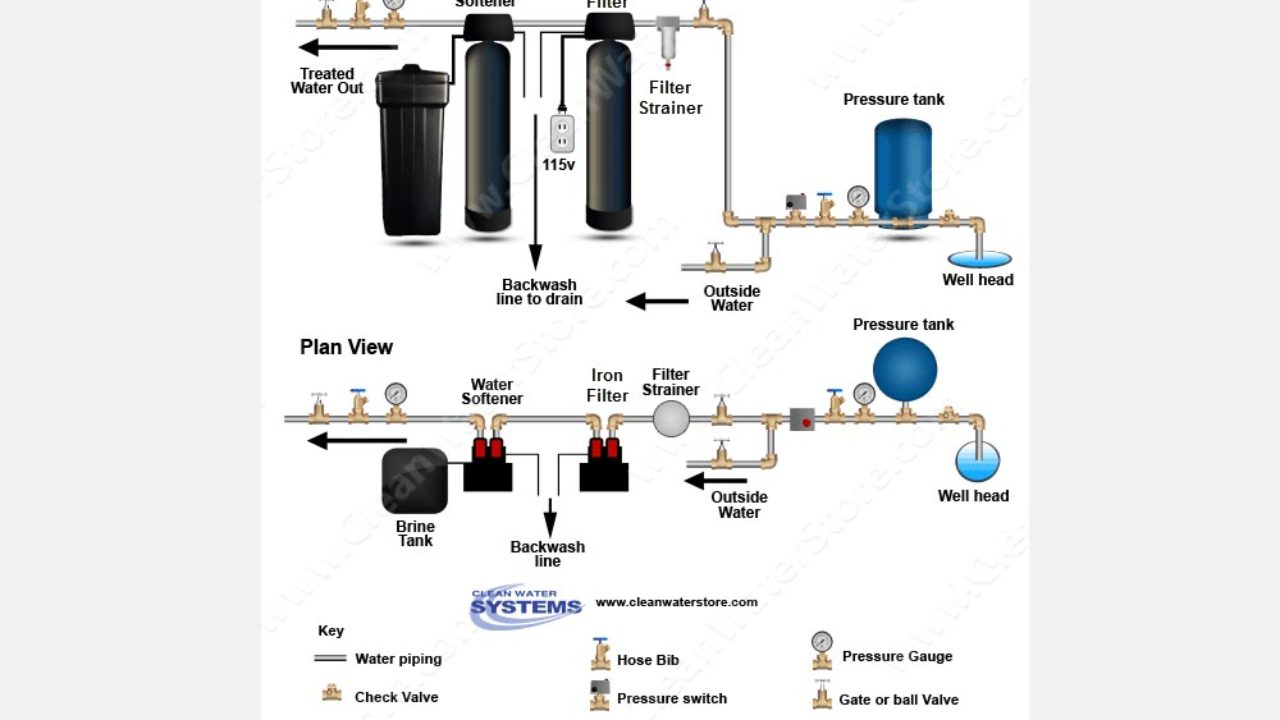
The iron and manganese are then removed from the softener resin bed through backwashing and regeneration. When tds is high other minerals in the water compete with the manganese for space on the resin and can even displace manganese which has attached to the resin. Thereafter the backwashing process can remove the metals from the softening filtering resin. The media lasts for many years often 15 to 20 years and these systems can filter the water at a faster rate.
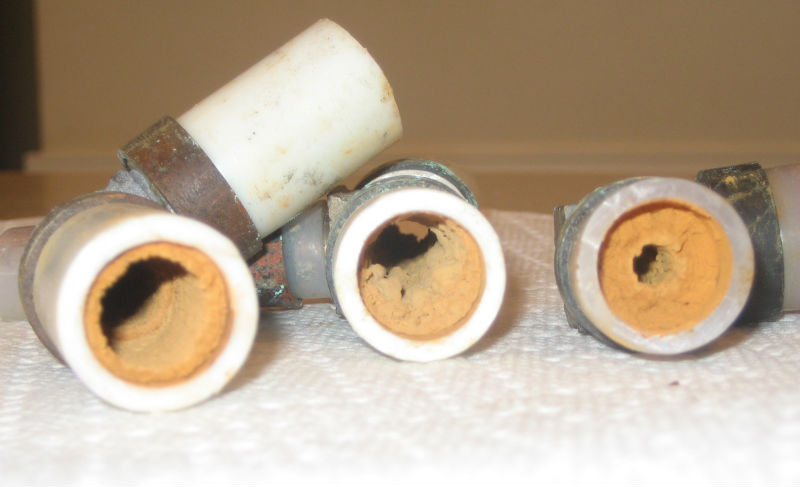
Additionally manganese removal can only commence when the iron has been completely removed. Removal of iron and manganese from water. Although generally used to remove minerals such as calcium and magnesium water softeners also demonstrate a strong ability to remove manganese in its unprecipitated form. This is the first report in the literature on the utilization of current modified biological waste as a biosorbent substance for the removal of manganese ions from the water environment.
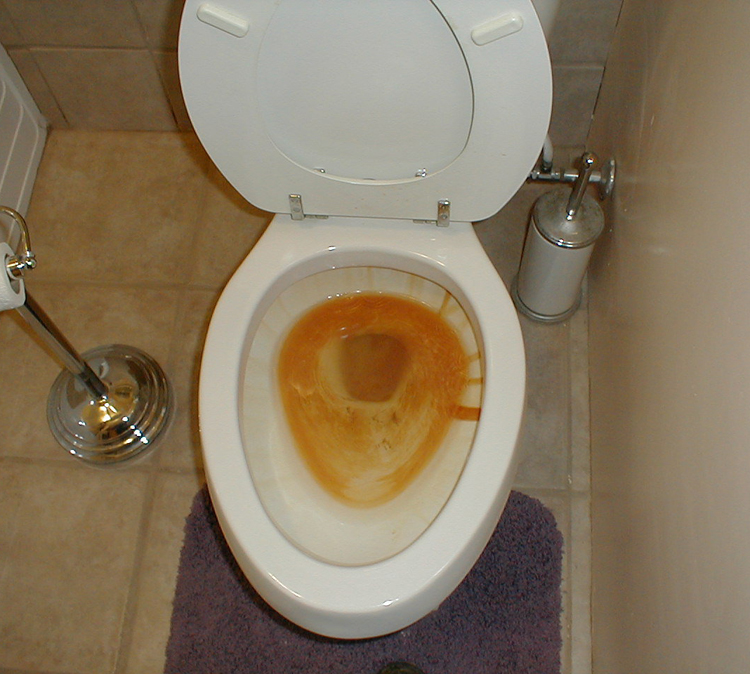
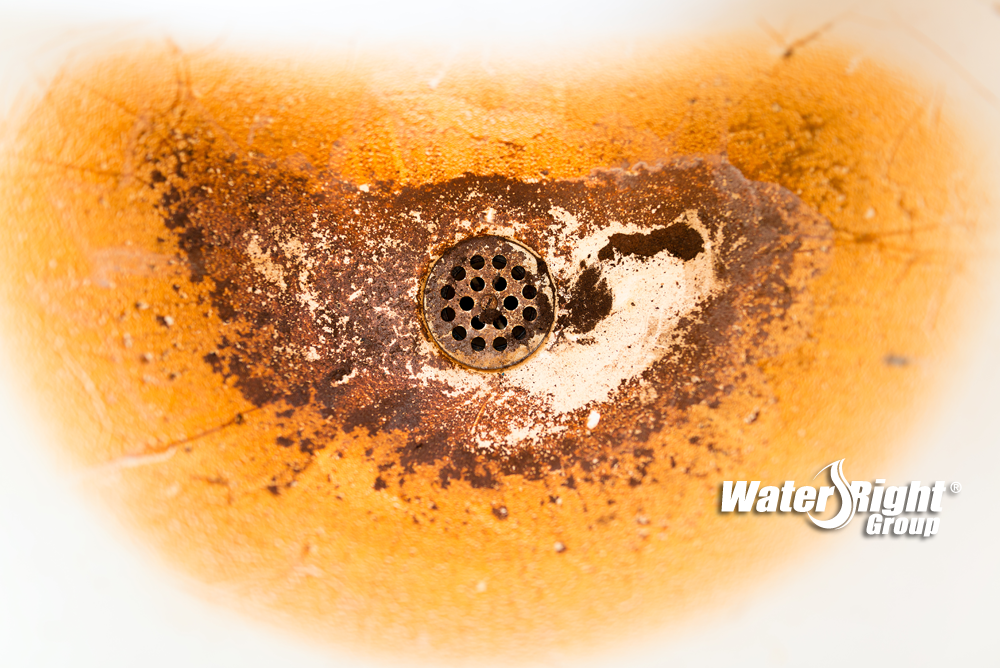
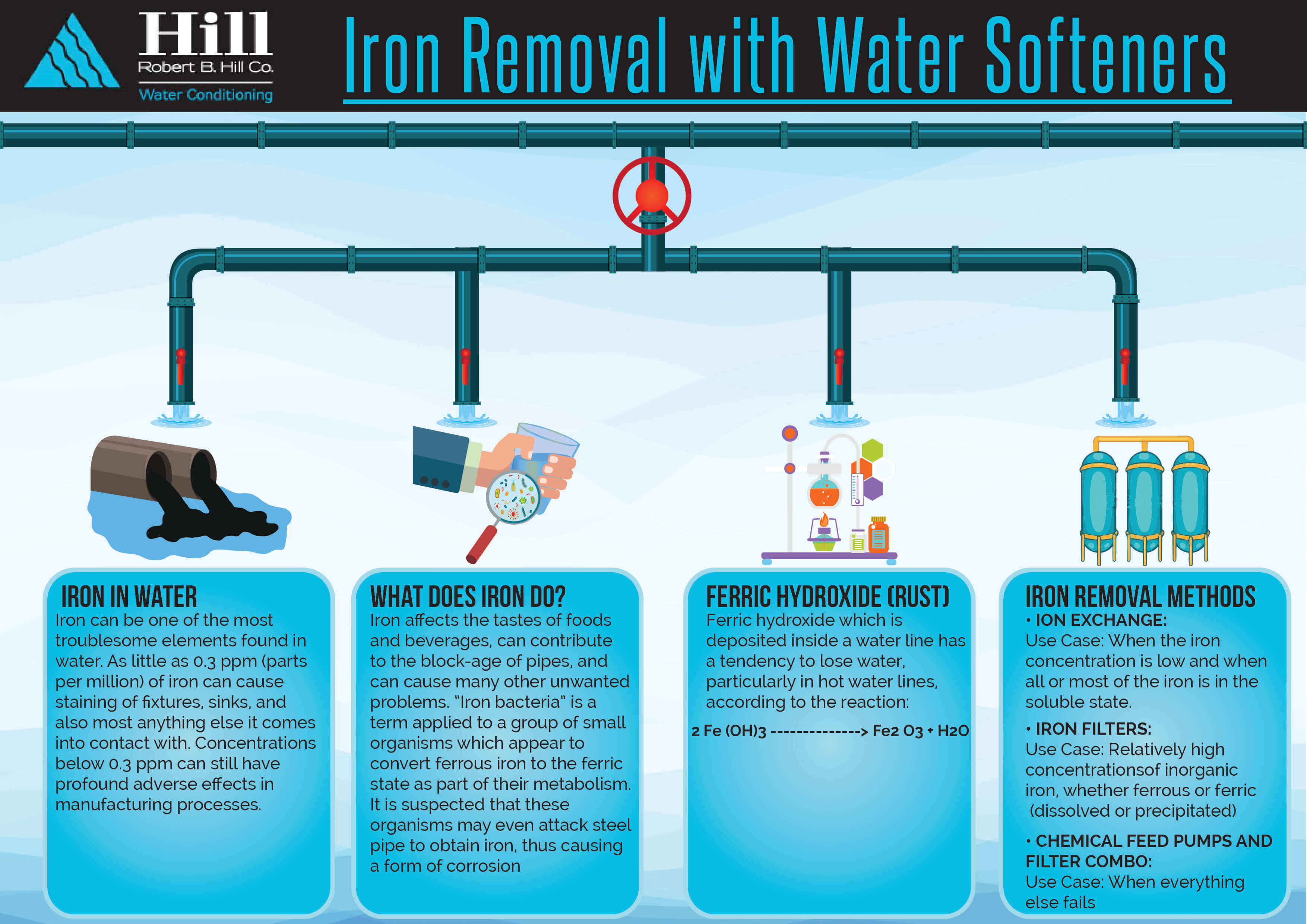
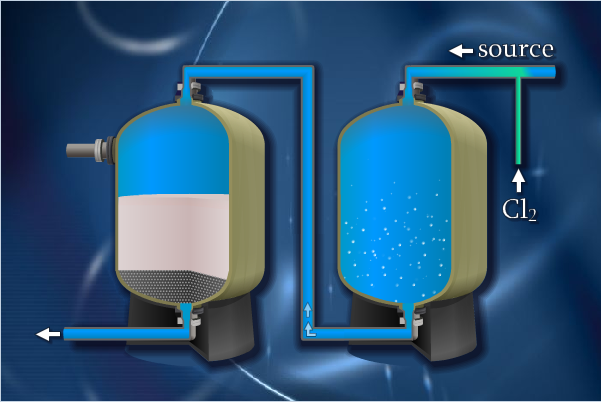
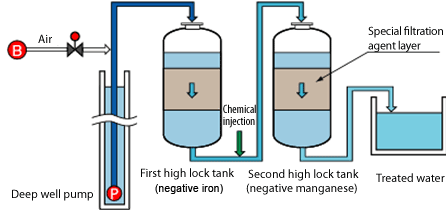
Iron and manganese in drinking water fsfedus. Adverse effects of higher fe and mn concentrations in. When water contains both iron and manganese there is a need to satisfy different redox potential conditions in order to oxidise both of these elements biologically figure 28. Water softeners work by means of ion exchange imparting the manganese molecules with a charge that causes them to cling tightly to resin beads in the softener.
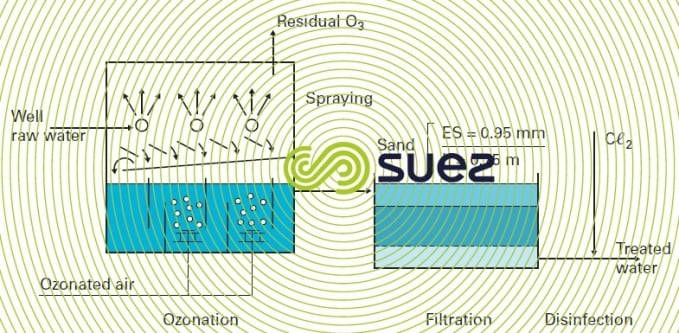
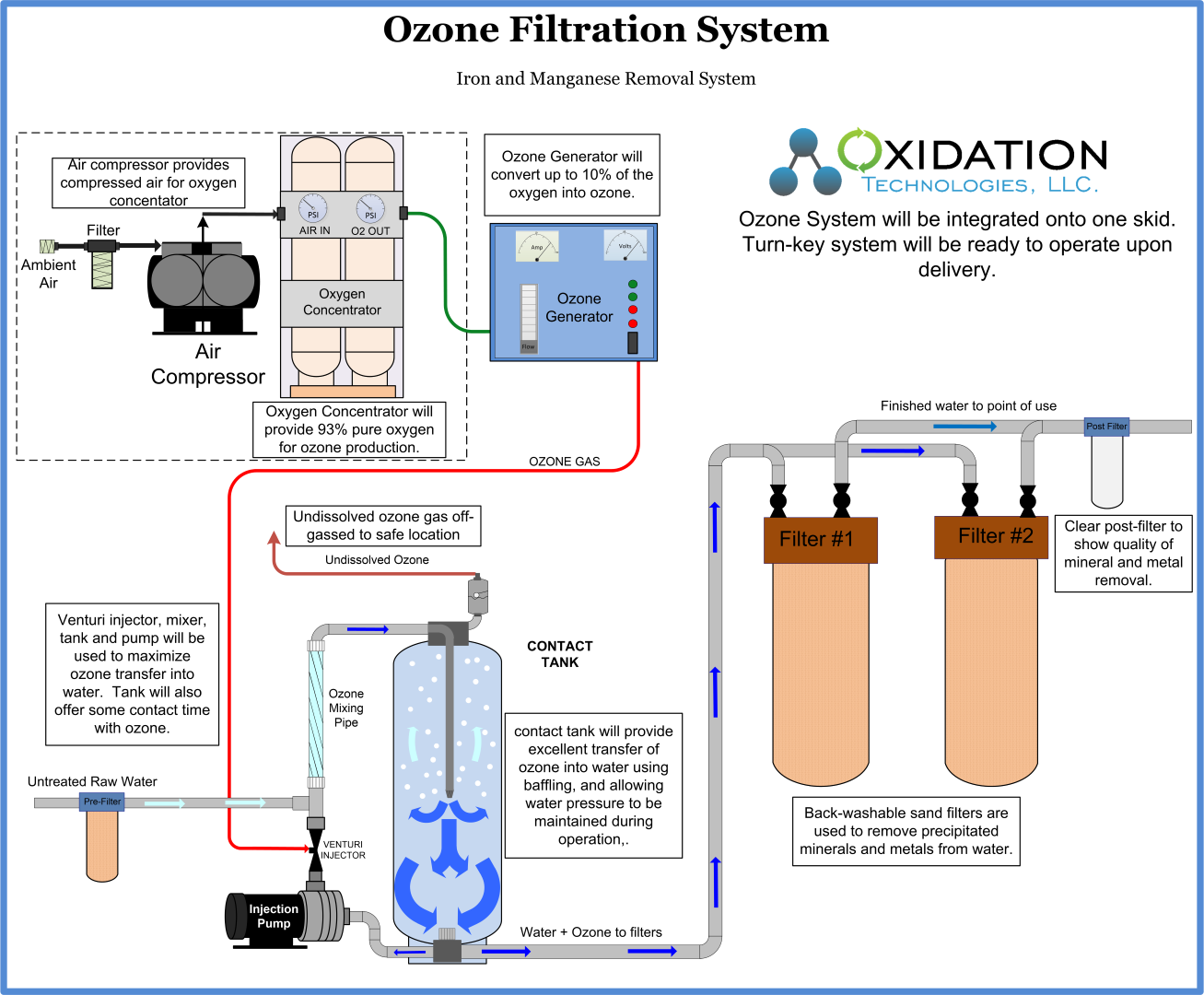
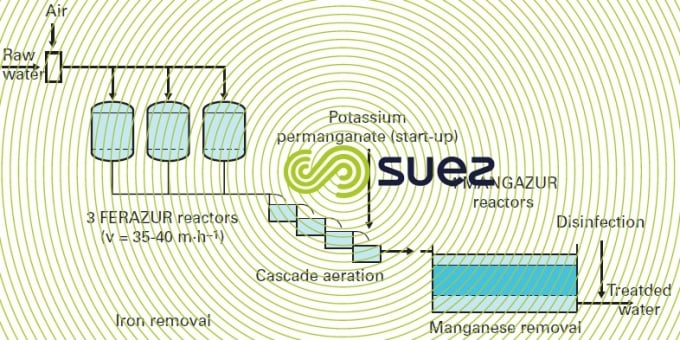
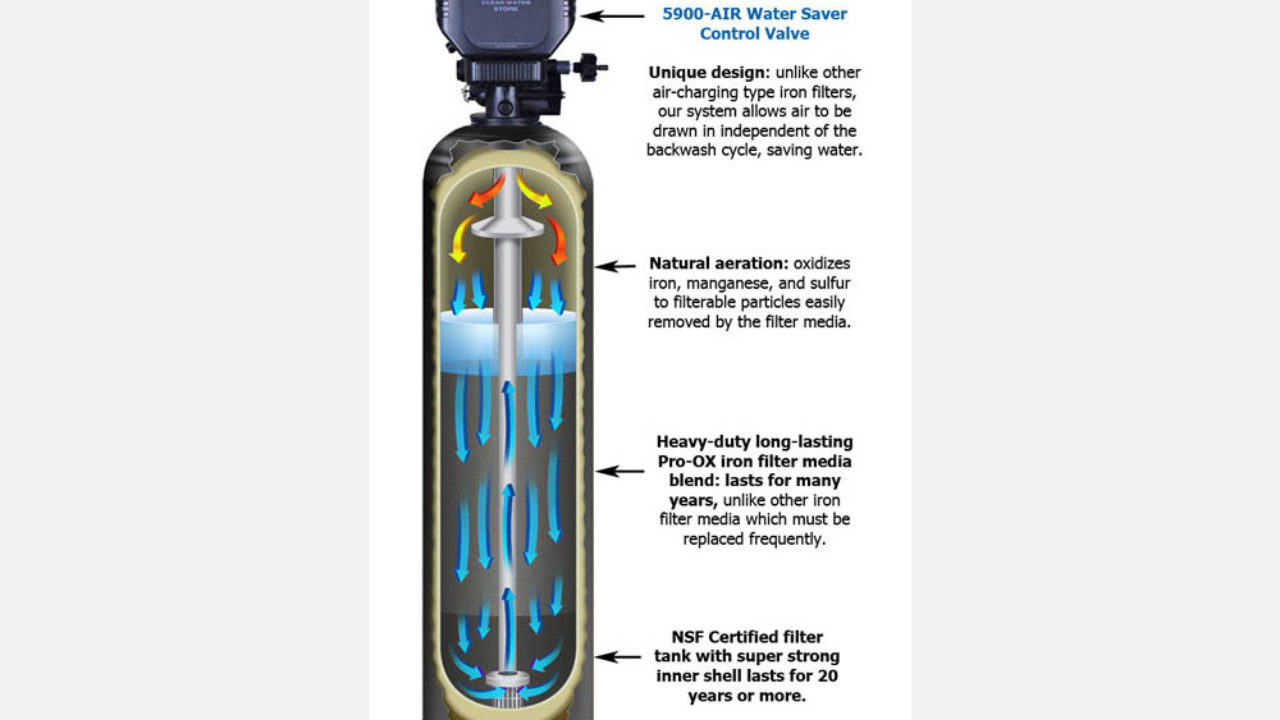
The solid manganese dioxide types of filter media are the gold standard for iron filtration media. Iron and manganese in drinking water. These elements can be removed during softening with lime but most commonly iron and manganese is removed by filtration after oxidation with air potassium permanganate or chlorine. The removal efficiencies of the water softeners vary depending on the ph level iron concentration and the water hardness.
Softeners remove manganese best if the total dissolved solids tds of the water is low. These systems can filter the water at a faster rate. Iron and manganese removal is accomplished in the same way by exchanging the iron and manganese for sodium. Is used to coat greensand and anthrasand with manganese oxide giving it a catalytic effect.
Water softeners use an ion exchange process during which the iron and manganese are replaced with sodium. The media lasts for many years often 15 to 20 years. 500 ppm tds works best for manganese removal by a water softener.













































































/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/19816580/qa-rusty-water.0.jpg)









