Manganese Deficiency In Corn Plants
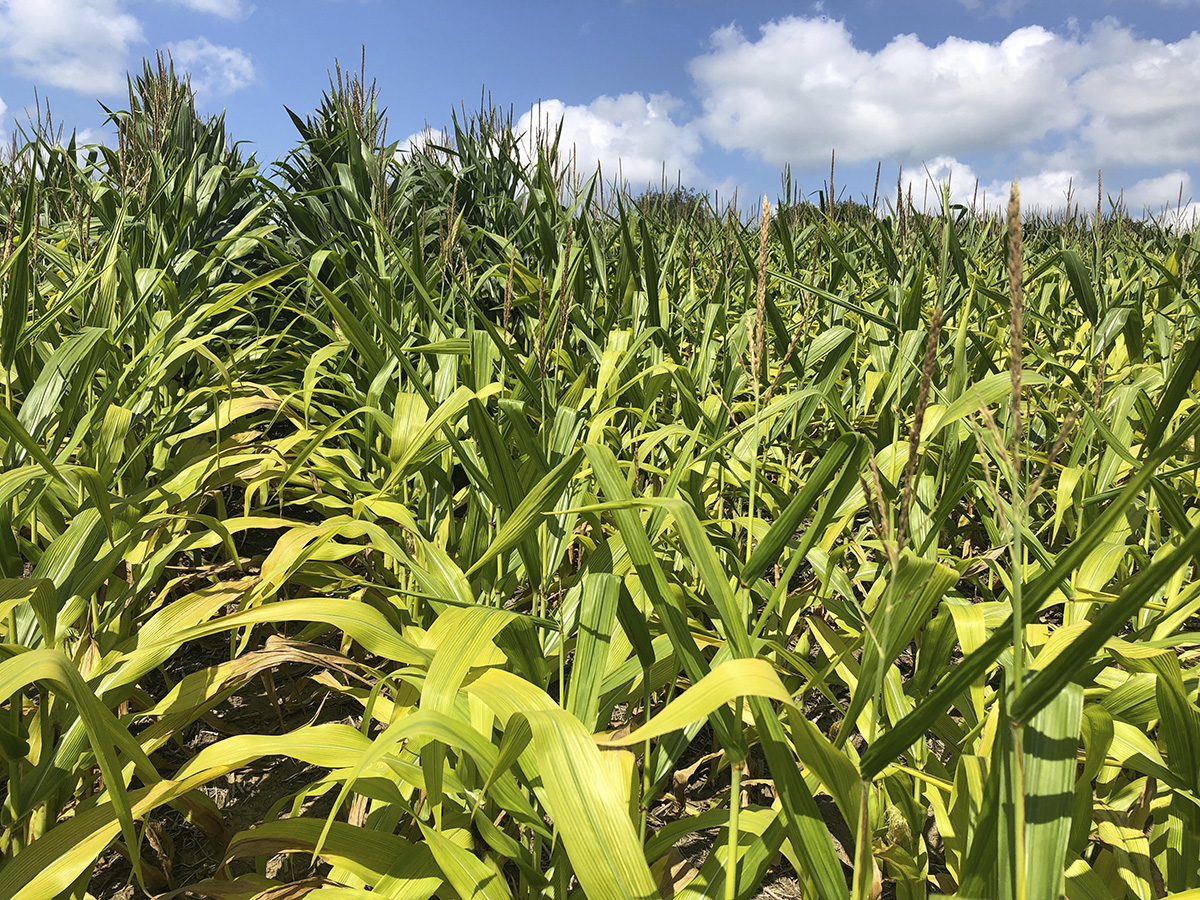
Soil is a dynamic system and can change rapidly spatially and temporally.

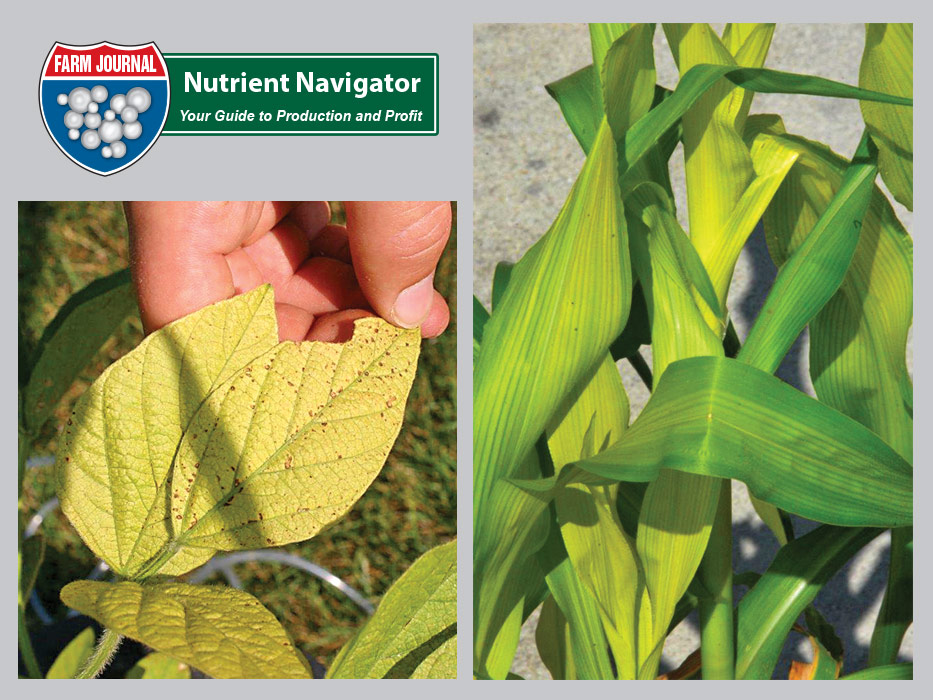
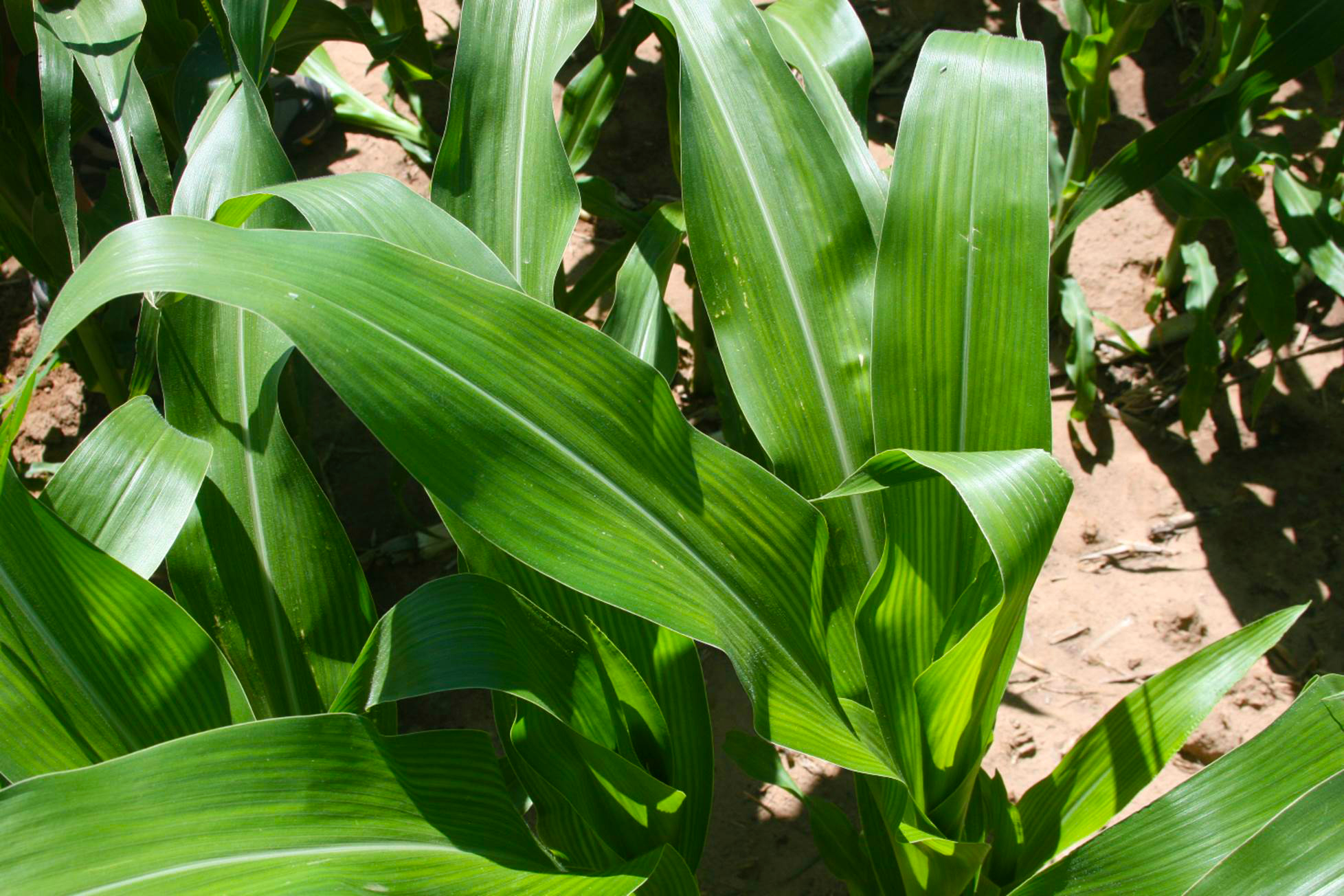
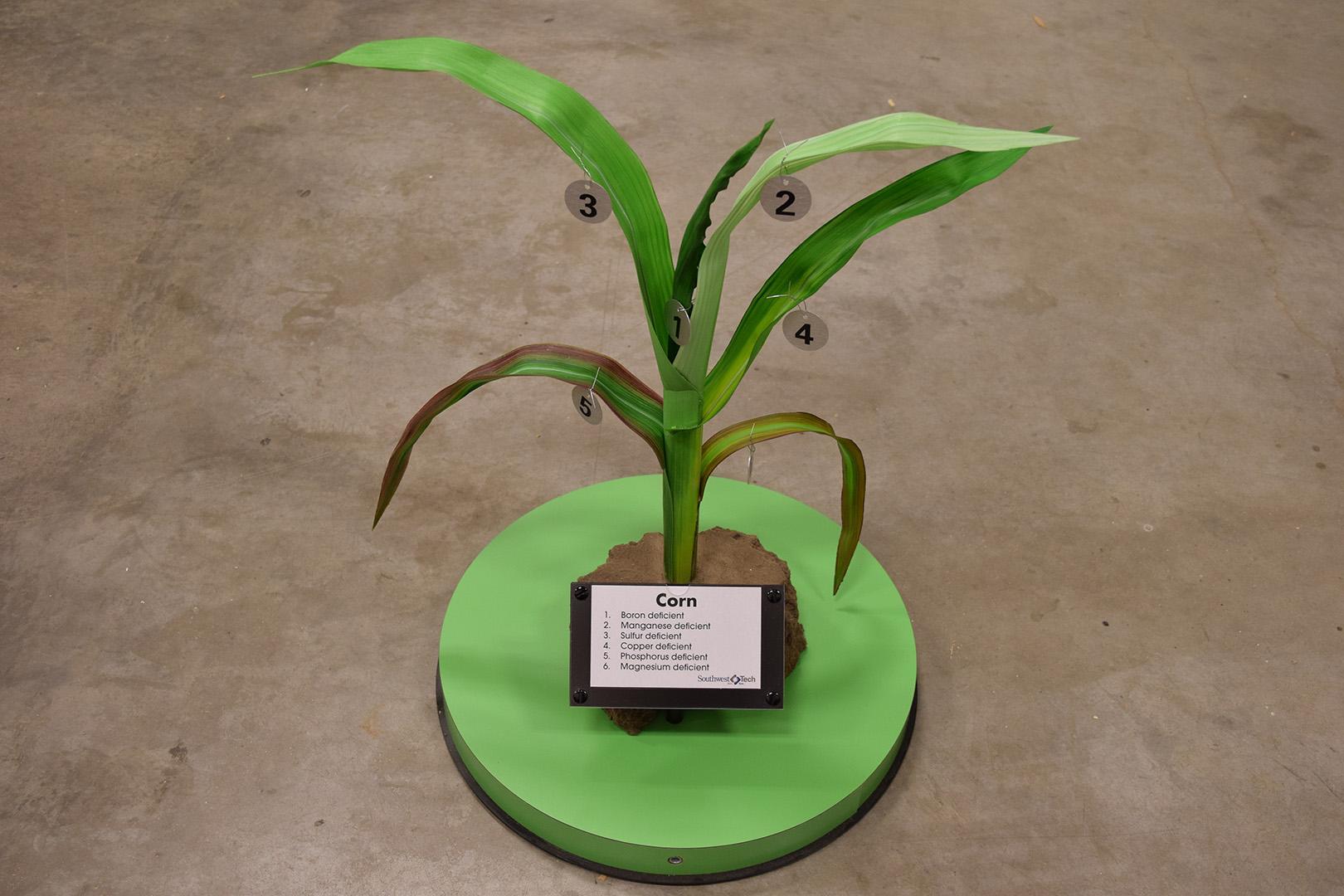
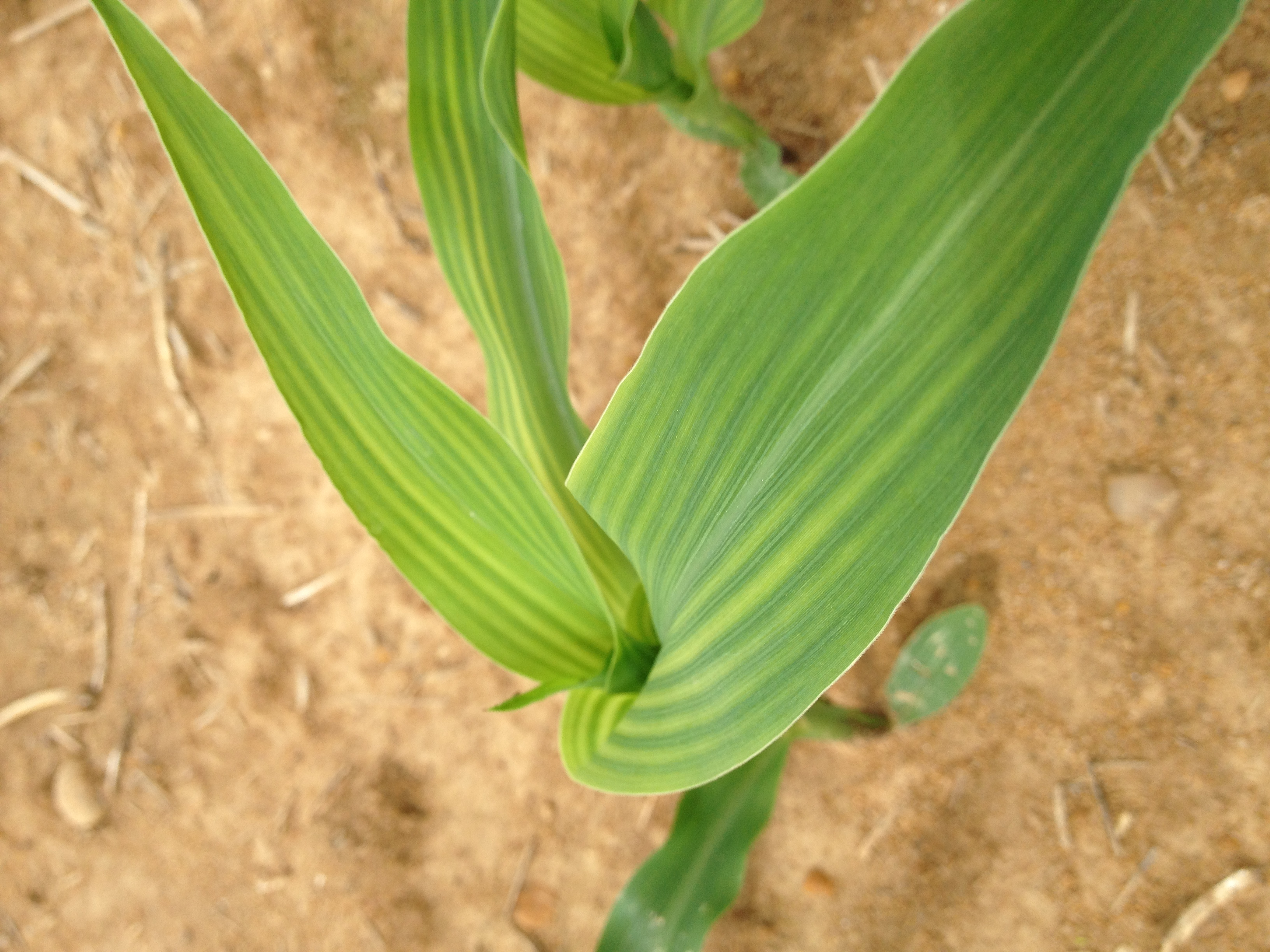
Manganese deficiency in corn plants. Older leaves suffer first and will die if theyre not given any treatment. Manganese deficiency is a widespread problem most often occurring in sandy soils organic soils with a ph above 6 and heavily weathered tropical soils. Manganese is highly immobile in the plant so mn deficiency symptoms are first seen in the young leaves. Dark yellow chlorosis advancing along purple color courtesy of the international plant nutrition institute phosphorus deficiency.
Your plant may also exhibit signs of a manganese deficiency if the ph is too high or if the plant is getting too much iron. Corn has a medium mn requirement. Most common in poorly drained soils also where organic matter levels are high. Learn how to manage your ph when growing cannabis.
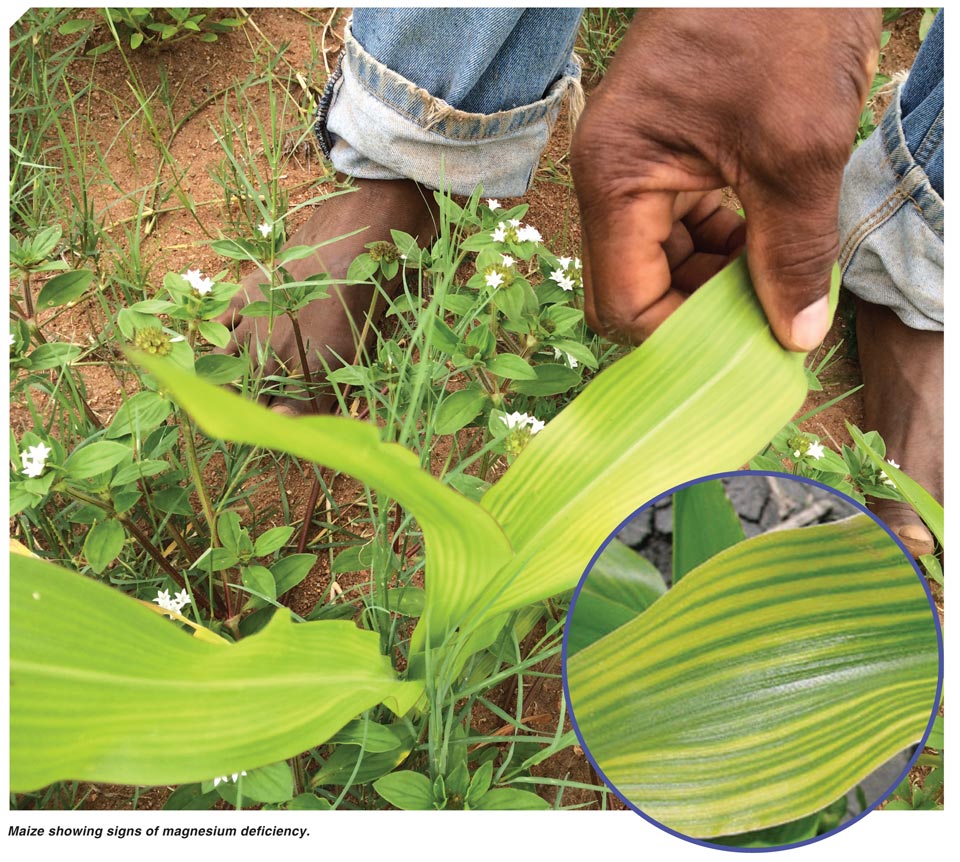
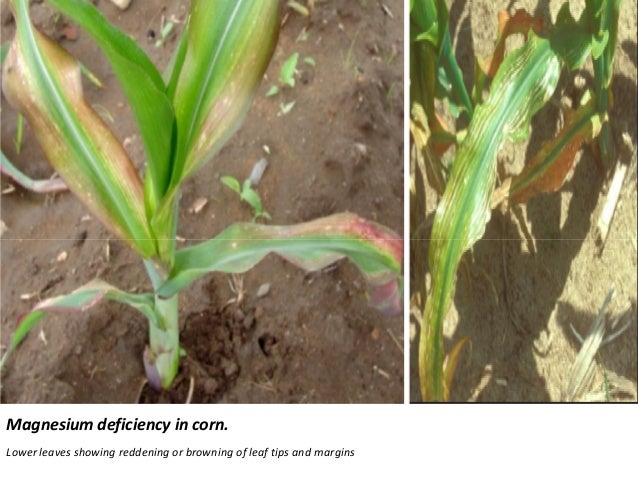
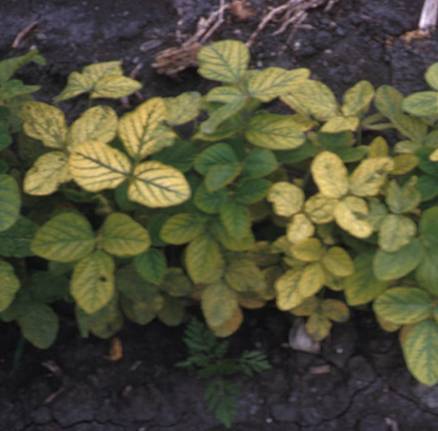
Magnesium is needed to give leaves their green colour so when theres a deficiency yellow breaks through between the veins and around the leaf edges instead. Manganese may be unavailable to plants where ph is high. Magnesium deficiencies can be dependent on year to year or month to month changes in growing conditions or fertilizer additions k nh4 plant mineral tissue analysis. It may take more than one of the specific situations above to induce magnesium deficiency.
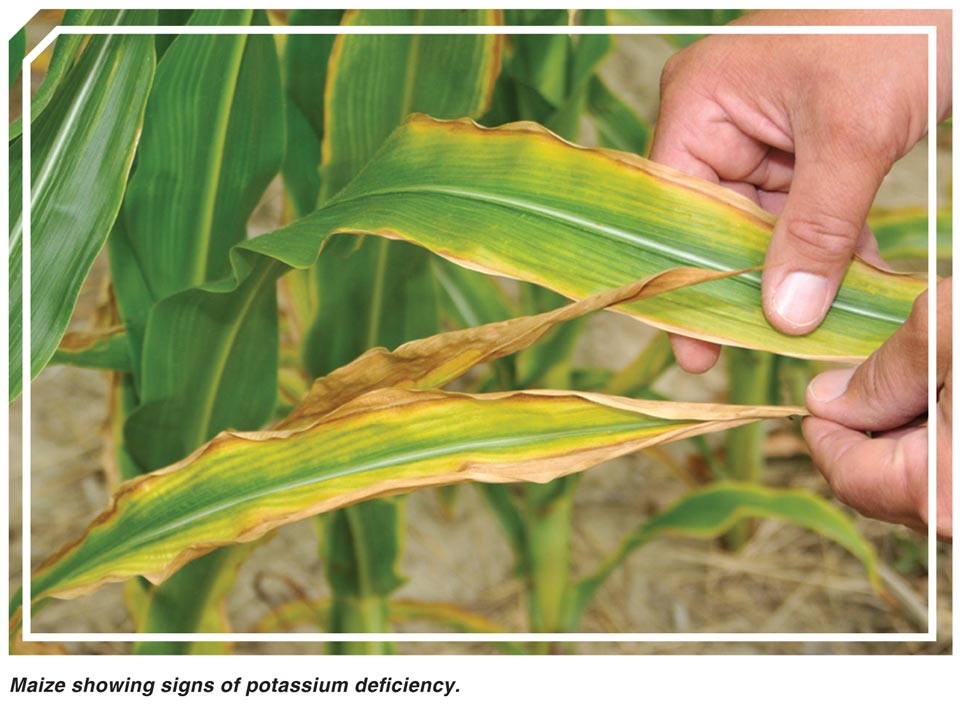
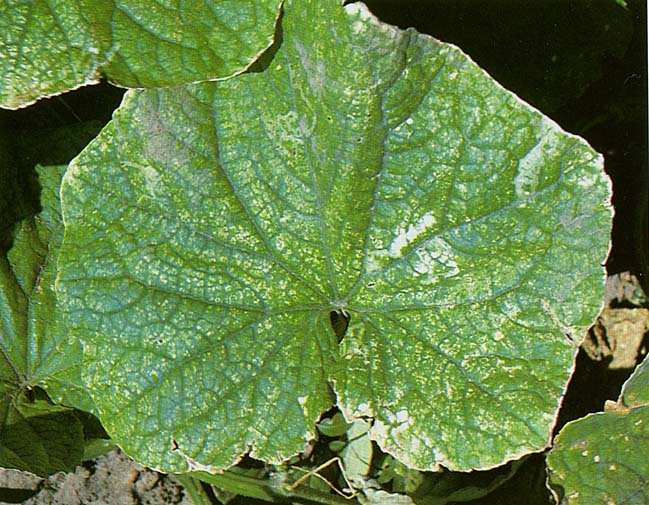
Other colours such as purple brown or red might also appear. Manganese in crop production manganese mn is an essential plant mineral nutrient playing a key role in several physiological processes particularly photosynthesis. In corn the chlorosis turns white so dead spots show up in the tissue between the veins manganese toxicity the opposite of deficiency because it results from excessive manganese is. Identify if you corn is suffering from nutrient deficiencies and learn more about the symptoms and causes and how to correct the deficiency.
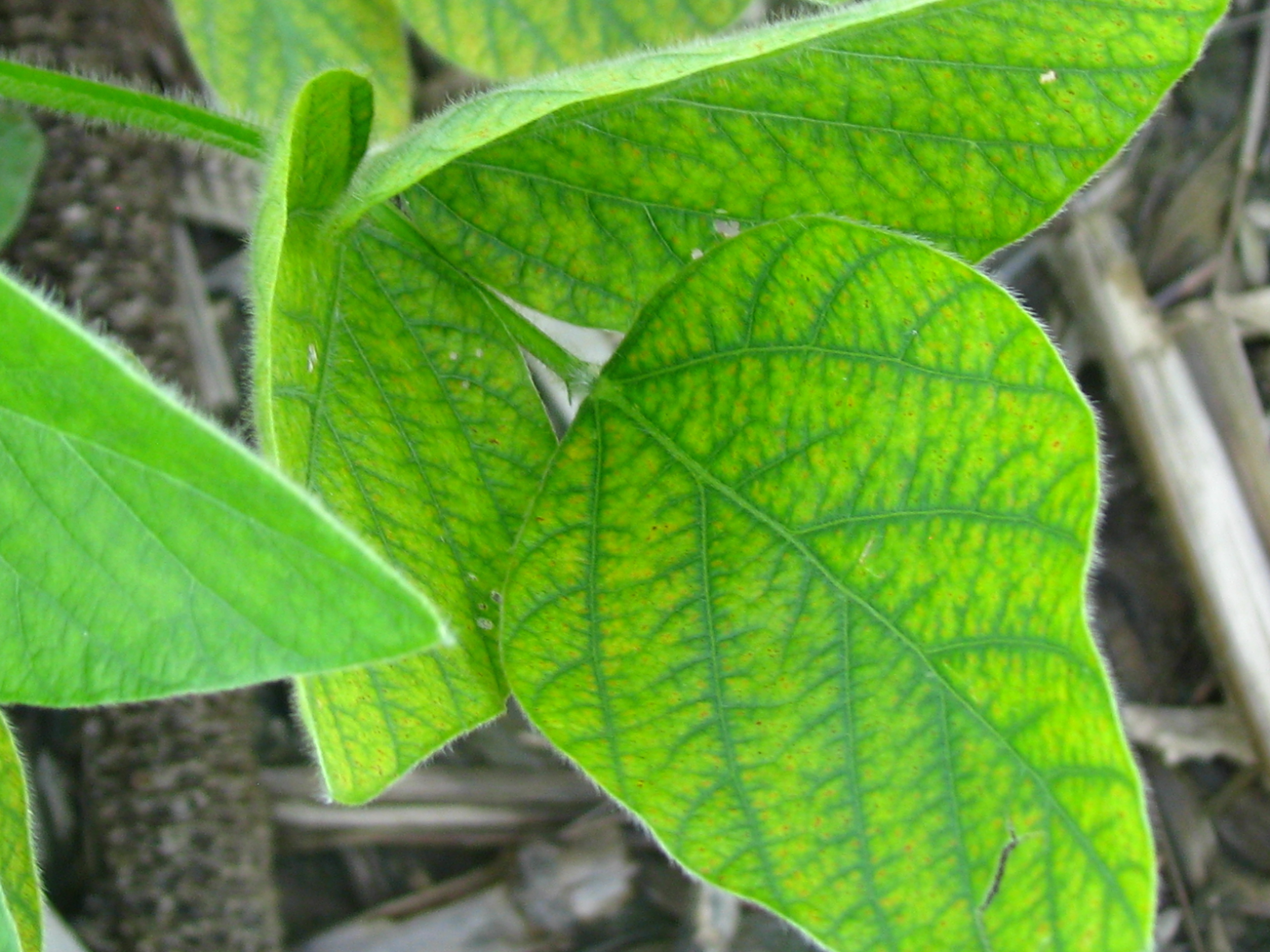
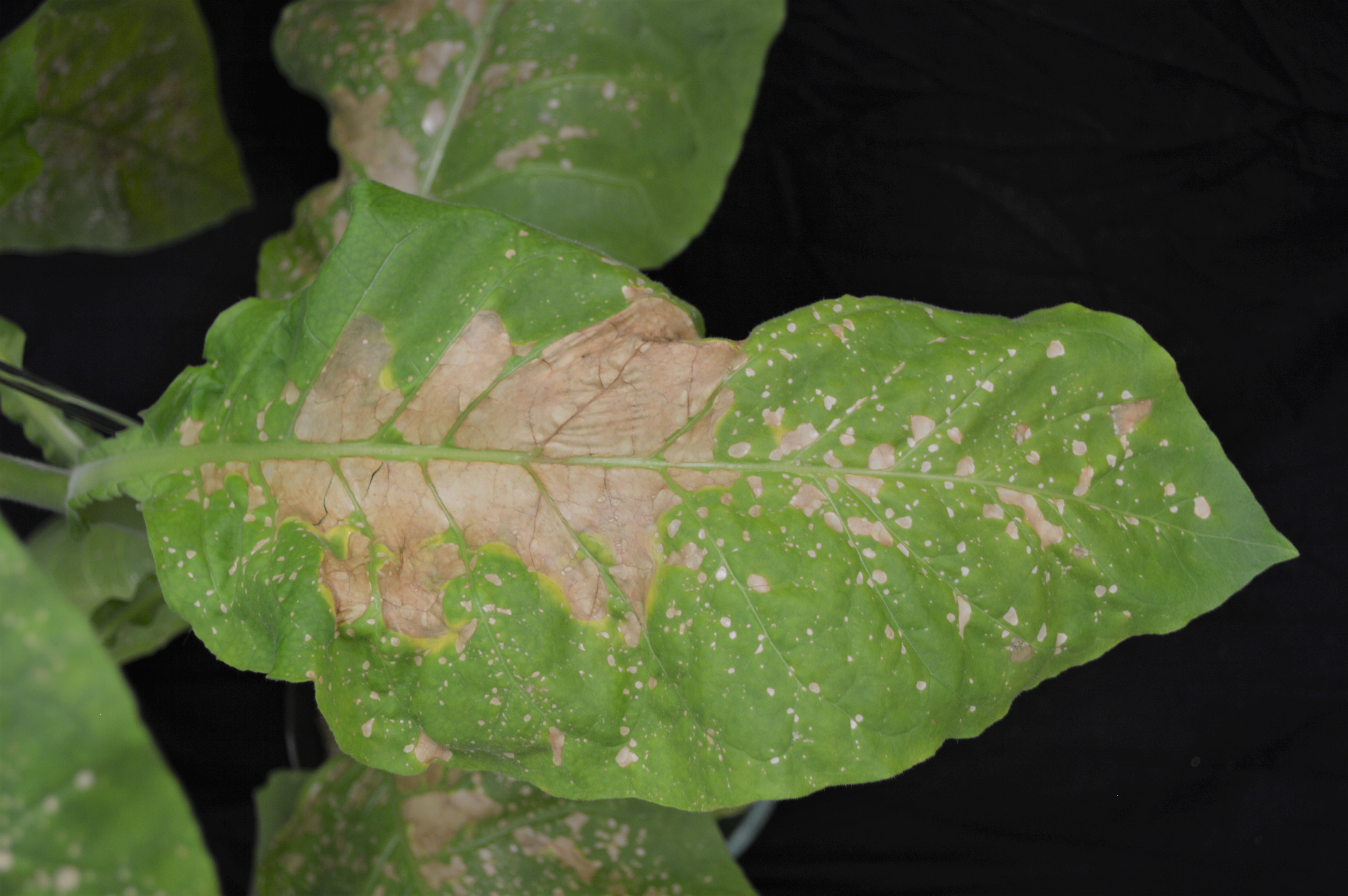
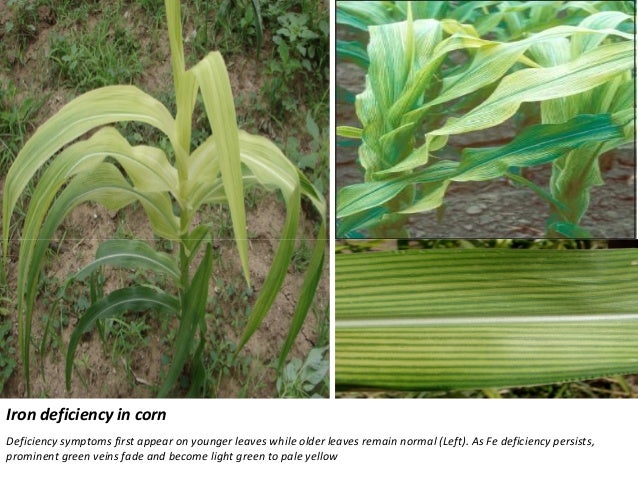
Manganese mn deficiency is a plant disorder that is often confused with and occurs with iron deficiency. A mn deficiency is recognized by interveinal chlorosis yellowing between the veins of the leaves while the veins themselves remain dark green figure 1. After a manganese deficiency is cleared up the problem brown spots and yellowing leaves will stop spreading to other growth usually within a week.